The greater Triangle area—including the cities of Raleigh and Durham—is one of the fastest-growing metros in the county. Raleigh’s population increased 48% between 2000 and 2012, making it the fastest-growing city in the U.S. over that time. Affordable housing pressures have come with such strong population growth, and affordability was recently a campaign issue in both Raleigh and Chapel Hill. As the Triangle continues to grow, policy-makers, planners, and developers must work to ensure that its neighborhoods remain economically and socially integrated.
Author: laurenprose
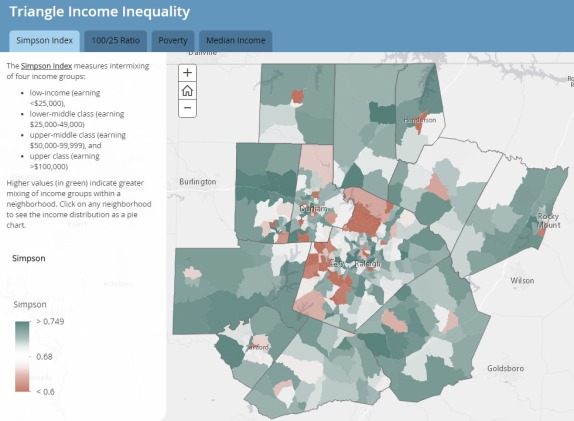
Measuring Income Mixing and Inequality in North Carolina
The Center for Urban & Regional Studies at the University of North Carolina Chapel Hill is thrilled to announce the launch of our new blog, Urban 2 Point 0. Focusing on urban issues relevant to North Carolina and beyond, Urban 2 Point 0 will present easily digestible data analysis complemented by infographics, maps, and other visuals. In our first series of posts, we’ll look at income mixing across neighborhoods in North Carolina’s three largest metro areas: Charlotte, the Triangle (Raleigh-Durham), and the Triad (Greensboro and Winston-Salem). We hope to show not only the level of mixing within each metro, but also income inequality across neighborhoods—that is, where poor or wealthy households are concentrated.
*
North Carolina is home to some of the fastest-growing cities in the nation (click image below for link to interactive map). Between 2000 and 2012, the Raleigh metro area grew faster than any large city, while Charlotte was close behind, ranking 5th. Largely due to its growing cities, North Carolina’s population exceeded the 10 million mark in 2015.